Iron deficiency (ID) is described in approximately half of the patients with stable chronic heart failure (HF),1 and up to 80% of patients admitted with acute HF (AHF).1,2 ID is responsible for reduced exercise tolerance, affects quality of life and results in higher rates of hospitalizations and death in HF patients.3 Therefore, is a well-recognized therapeutic target in patients with ID and stable HF.4 Current HF-guidelines recommend ID testing in newly diagnosed HF and during outpatients monitoring.4 However, there is not a specific recommendation in AHF.4
The recent AFFIRM-AHF trial showed that intravenous iron supplementation in patients with ID and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <50% stabilized after an episode of AHF reduced the risk of HF-hospitalizations.5
In this study, we aimed to evaluate the frequency, evolution over the years, and clinical factors associated with ID testing in patients with AHF.
This is a consecutive retrospective multicenter study conducted from 1 September 2014, to 1 September 2019, that included 3555 patients admitted for AHF in 3 third-level hospitals in Spain. By design, patients with acute coronary syndrome or intravenous iron therapy were excluded. Information related to demography, medical history, vital parameters, 12-lead electrocardiogram, standard laboratory tests (including ferritin and transferrin saturation), echocardiographic parameters, and pharmacological therapies was recorded. Anemia was defined as a hemoglobin level <12g/dL in women and <13g/dL in men. ID was defined as ferritin <100μg/L and/or transferrin saturation <20% if ferritin 100–299μg/L.4 This study conformed to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by an institutional review committee [Comité Ético de Investigación Clínica, Fundación Investigación del Hospital Clínico Universitario de Valencia (INCLIVA)].
Continuous variables were expressed as mean±standard deviation or median (interquartile range) when appropriate. Discrete variables were summarized as percentages. Logistic regression was used to analyze the factors associated with ID assessment. A final model was derived by using backward stepwise selection. The linearity assumption for all continuous variables was simultaneously tested, and the variable transformed, if appropriate, with fractional polynomials. R2 evaluated the contribution of the covariates to the variability of the model.
Covariates included in the final multivariate model were age, gender, history of myocardial infarction, chronic renal failure, first admission for AHF, admission center, calendar year of admission, peripheral edema, heart rate, hemoglobin, estimated glomerular filtration rate, serum sodium, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and LVEF. The discriminative ability of the multivariate model evaluated by the area under the receiving operating curve was 0.705.
The mean age was 74.6±11.0, 1610 (45.2%) patients were women, 1628 (45.8%) showed LVEF<50%, and 1812 (51.0%) showed anemia. Measurement of ferritin and transferrin saturation was performed in 1700 (47.8%) patients. Isolated ferritin and transferrin saturation measurements were performed in 2402 (67.6%) and 1700 (47.8%) patients, respectively. Baseline characteristics across ID evaluation are shown in Table 1. Overall, ID assessment was more frequent in younger, diabetic patients, those without prior AHF admissions, higher heart rate and lower diastolic blood pressure, those with LVEF<50%, and in more congestive patients (pleural effusion, peripheral edema, New York Heart Association class III–IV before admission, and lower serum sodium values). Among those with ID assessment, ID was found in 1246 (73.3%) patients, without differences between LVEF status (71.6% in patients with LVEF<50% vs 74.9% in those with LVEF≥50%; P=.124). The rate of ID testing stepwise increased from 36.2% in 2014 to 54.7% in 2019, P<.001.
Baseline characteristics across ID testing.
| Variables | All (n=3555) | No ID assessmentc (n=1855) | ID assessmentc (n=1700) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics and medical history | ||||
| Age, years | 74.6±11.0 | 75.1±11.1 | 74.1±10.9 | .011 |
| Gender (male), n (%) | 1945 (54.7) | 991 (53.2) | 954 (56.1) | .107 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 2849 (80.1) | 1505 (81.1) | 1344 (79.1) | .122 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 1573 (44.2) | 781 (42.1) | 792 (46.6) | .007 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 1966 (55.3) | 1000 (53.1) | 966 (56.8) | .081 |
| Smoker, n (%) | 420 (11.8) | 204 (11.0) | 216 (12.7) | .115 |
| Prior smoker, n (%) | 1071 (30.2) | 546 (29.5) | 525 (30.9) | .363 |
| IHD, n (%) | 1123 (31.6) | 606 (32.7) | 517 (30.4) | .148 |
| Valve heart disease, n (%) | 1295 (36.4) | 663 (35.7) | 632 (37.2) | .374 |
| First admission for AHF, n (%) | 2486 (69.9) | 1121 (60.4) | 1365 (80.3) | <.001 |
| Charlson index, points | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–4) | .140 |
| Pleural effusion, n (%) | 1750 (49.2) | 877 (47.3) | 873 (51.3) | .015 |
| Peripheral edema, n (%) | 2260 (63.6) | 1122 (60.5) | 1138 (66.9) | <.001 |
| Vital signs | ||||
| Heart rate, bpm | 94±27 | 92±27 | 97±27 | <.001 |
| SBP, mmHg | 141±29 | 141±29 | 141±29 | .848 |
| DBP, mmHg | 79±18 | 78±18 | 80±19 | .001 |
| Electrocardiogram | ||||
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 1674 (47.1) | 845 (45.5) | 829 (48.8) | .055 |
| BBB, n (%) | 1171 (32.9) | 614 (33.1) | 557 (32.8) | .832 |
| Echocardiography | ||||
| LVEF, % | 49.4±15.2 | 50.6±15.3 | 48.2±15.1 | <.001 |
| LVEF<50%, n (%) | 1628 (45.8) | 808 (43.6) | 820 (48.2) | .005 |
| LAD, mm | 44.5±7.5 | 44.5±7.6 | 44.5±7.4 | .981 |
| PASP, mmHga,b | 43 (35–52) | 44 (35–54) | 42 (34–51) | .011 |
| Laboratory data | ||||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 12.4±2.0 | 12.4±2.0 | 12.3±2.0 | .342 |
| Hematocrit, % | 38.8±6.2 | 39.0±6.0 | 38.7±6.2 | .553 |
| Anemia (WHO criteria), n (%) | 1812 (51.0) | 937 (50.5) | 875 (51.5) | .568 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.27±0.70 | 1.28±0.74 | 1.27±0.66 | .569 |
| eGFR (MDRD formula), mL/min/1.73m2 | 63.6±28.2 | 62.7±26.9 | 64.7±29.5 | .032 |
| Serum sodium, mEq/L | 138±4 | 139±4 | 138±4 | <.001 |
| Serum potassium, mEq/L | 4.3±0.6 | 4.3±0.6 | 4.3±0.6 | .115 |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mLa | 3917 (1920–8292) | 3772 (1937–7807) | 4065 (1900–8758) | .077 |
AHF, acute heart failure; BBB, bundle branch block; CA125, carbohydrate antigen 125; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; ID, iron deficiency; IHD, ischemic heart disease; LAD, left atrial diameter; MDRD, modification of diet in renal disease; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; NYHA, New York Heart Association; PASP, pulmonary artery systolic pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; TAPSE, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion; TSAT, transferrin saturation; WHO, World Heart Organization.
Values for continuous variables are expressed as mean±standard deviation.
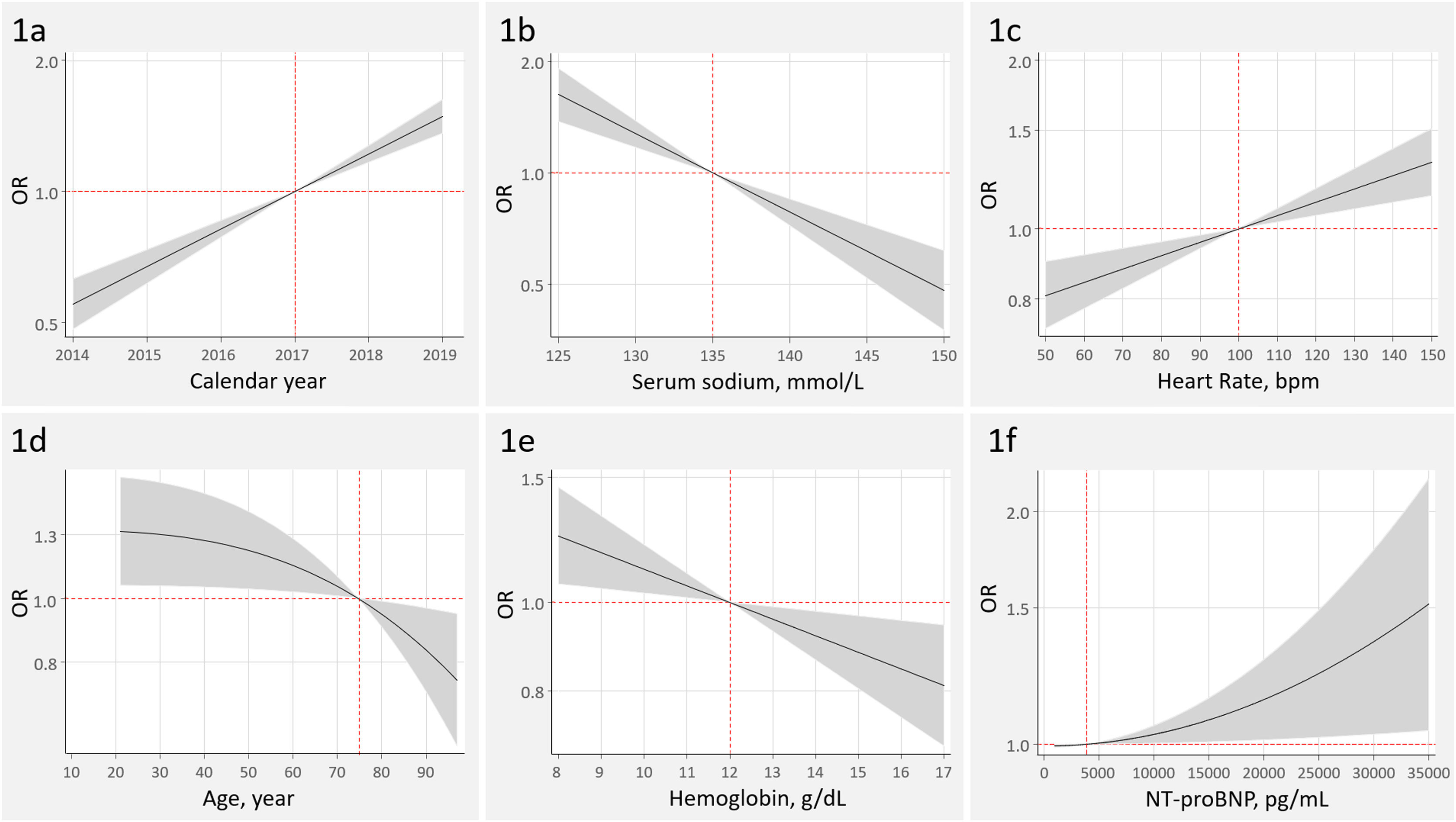
The 2 most important covariates, explaining 70% of the model variability, were first AHF-admission (R2, 37.4%; P<.001) and calendar year (more recent admissions) (R2, 33.1%; P<.001) (Fig. 1A). Patients with a first admission displayed a three-fold increased probability of ID testing [odds ratio (OR), 3.06; 95% confidence interval (95%CI), 2.60–3.61; P<.001].
Other covariates associated with higher odds of ID testing were, in order of importance, lower values of serum sodium (R2, 10.0%; P<.001), admission center (R2, 4.7%; P<.001), peripheral edema (R2, 4.6%; P<.001), heart rate (R2, 2.4%; P<.001), history of myocardial infarction (R2, 1.8%; P=.023), age (R2, 1.5; P=.015), and hemoglobin (R2, 1.2; P=.007) (Fig. 1B–E).
Higher NT-proBNP was independently associated with the odds of ID testing, with a however, marginal contribution to the model's predicatibility (R2<0.01%; P=.030) (Fig. 1F). LVEF<50% (OR, 1.13; 95%CI, 0.97–1.33; P=.117) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (OR, 1.03; 95%CI, 0.99–1.06; P=.056 per increase in 10mL/min/1.73m2) were not independently associated with ID testing.
In the present study, performed in a representative contemporary cohort of patients with AHF, ID was tested in near 50% of the patients. ID assessment rates increased over the inclusion period, which emerged as the second most important variable, after the absence of a prior admission for AHF. Other factors associated with a higher odds of ID assessment were those related to greater severity of the episode. Of note, NT-proBNP and traditional factors associated with ID, such as lower hemoglobin, renal dysfunction, and left ventricular systolic dysfunction, were marginally or not associated with ID assessment.
Regarding these findings, some issues deserve to be highlighted. First, the most relevant factors associated with the odds of ID testing were the absence of a prior AHF hospitalization, the year of admission (a stepwise increase over the years), and greater signs of congestion. In the absence of specific recommendations, we postulate the increase of the diagnostic/prognostic awareness resulting from these situations may explain these findings. Second, traditional risk factors for ID, left ventricular systolic dysfunction and NT-proBNP values did not emerge as relevant factors. The validation of the present results is endorsed by recent studies showing similar ID rates (about 70%–80% of patients).1,2
Some crucial limitations should be acknowledged. This is a retrospective observational in which important unmeasured confounders might be playing a relevant role. Indeed, the model has a limited discriminative capacity, suggesting that many variables have not been taken into account. Furthermore, this study only included three sites in Spain. Thus, the external validation of the present findings needs to be confirmed in contemporary registries.
ID assessment in patients with AHF remains low, despite increasing over the last years. Further HF-guidelines should expressly state a recommendation about ID testing in AHF syndromes.
FundingThis work was supported by unrestricted grants from Vifor Pharma and CIBERCV [grant number 16/11/00420]. The authors have no other funding, financial relationships, or conflicts of interest to disclose relative to this work.
Authors’ contributionsAll authors contributed substantially to the conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of the manuscript. G. Miñana and J. Núñez wrote the article. All authors made a critical review of its intellectual content and gave final approval to the version to be published. All authors agree to assume responsibility for all aspects of the article and to investigate and resolve any question related to the accuracy and veracity of any part of the work.
Conflicts of interestNone.