A 53-year-old male attended a scheduled clinic appointment due to severe aortic stenosis on a bicuspid valve who underwent surgical valve replacement eight years prior to current medical review. No complications during the postoperative period were reported.
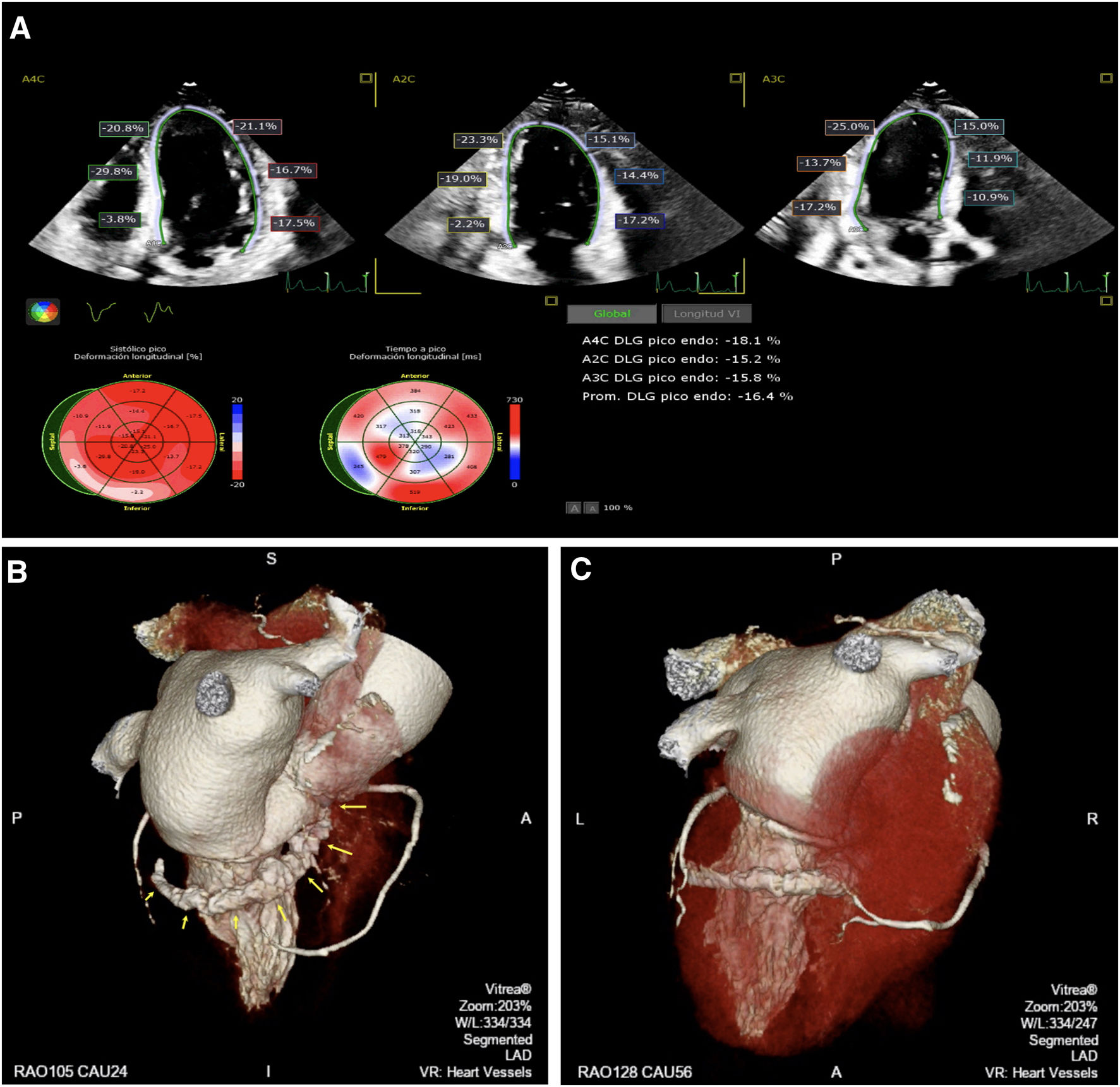
A three-dimensional (3D) echocardiography using the EPIQ CVx system (Philips Medical Systems, Andover, United States) revealed a calcified intramyocardial deposit located in the mid-basal inferoseptal, and basal inferolateral segments of the left ventricle (LV). Overall LV function was preserved (Video 1 of the supplementary data). Two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography showed a borderline LV global longitudinal strain value, mainly due to basal anteroseptal, inferoseptal and inferior segments (Fig. 1A; Video 2 of the supplementary data).
A contrast-enhanced multidetector computed tomography (CT) and 3D volume-rendering (3DVR) post-processing was performed, showing a tubular intramyocardial calcification that originated adjacent to the right edge of the aortic prosthesis and extended in a spiroid intramurally trajectory (Fig. 1B [3DVR with elimination of surrounding myocardial tissue] and Fig. 1C; Videos 3 and 4 of the supplementary data).
Intramyocardial dissecting hematoma is an unusual form of incomplete cardiac rupture most often seen after myocardial infarction, cardiac surgery, and severe thoracic injury, which may lead to myocardial rupture or pseudoaneurysm formation. This incidental finding corresponded to a mild postsurgical calcified intramyocardial dissecting hematoma. No specific treatment was given in response to this complication as it remained undetected in the immediate postsurgical period and evolved asymptomatically for many years. Multimodality noninvasive imaging techniques may help to diagnose this condition that needs a high level of suspicion, especially in mild hematomas. Patient gave informed consent to report his clinical case.
FundingAuthors do not have any funding sources.
Authors’ contributionsAll authors have participated in the work and have reviewed and agree with the content of the article.
Conflicts of interestAuthors report no relationships that could be construed as a conflict of interest.