Sacubitril/valsartan (SV) is recommended in patients with heart failure, especially in reduced ejection fraction. So far, the safety of its use in perioperative cardiac surgery is uncertain but given its mechanism of action and possible blood pressure lowering effect, some guidelines recommend discontinuation, without clear evidence. This systematic review aims to assess clinical outcomes of use SV in the perioperative period compared with never having used it or its withdrawal.
MethodsSystematic literature review in MedLine, Cochrane, EMBASE and LILACs of studies published in English and Spanish. We included randomized clinical trials and non-randomized studies evaluating adult patients undergoing cardiac surgery that compared the use of SV up to the day of surgery versus stopping or not starting it prior to the procedure. In-hospital and 30-day mortality, length of stay in general ward and intensive care unit stay, orotracheal intubation, postoperative vasoplegia and need for renal replacement therapy were assessed. Quality was assessed using the ROBINS tool.
ResultsThree non-randomized studies were included, one single-arm. There were fewer cases of in-hospital and 30-day mortality in the group in which SV was not discontinued, with no statistically significant difference. There was no difference in length of hospital or intensive care unit stay, orotracheal intubation, need for renal replacement therapy, or frequency of postoperative vasoplegia (OR, 0.77; 95%CI, 0.23–2.98).
ConclusionsThe current evidence is scarce and of low quality so a recommendation regarding the use of SV prior to cardiac surgery cannot be generated, further studies are required.
El sacubitrilo-valsartán (SV) está recomendado en pacientes con falla cardiaca, especialmente en caso de fracción de eyección reducida. Hasta ahora, no se sabe con certeza la seguridad de su uso en el perioperatorio de cirugía cardiaca, pero dado su mecanismo de acción y el posible efecto en reducción de la presión arterial, algunas guías recomiendan suspenderlo, sin evidencia clara al respecto. Esta revisión sistemática busca evaluar los resultados clínicos del uso de SV en el periodo perioperatorio en comparación con no haberlo usado nunca o su suspensión.
MétodosRevisión sistemática de la literatura en MedLine, Cochrane, EMBASE y LILACs de estudios publicados en español e inglés. Se incluyeron experimentos clínicos aleatorizados y estudios no aleatorizados que evaluaran pacientes adultos llevados a cirugía cardiaca, que compararan el uso de SV hasta el día de la cirugía frente a suspenderlo o no iniciarlo previo al procedimiento. Se evaluó mortalidad intrahospitalaria y a 30 días, duración de estancia hospitalaria en sala general y en cuidado intensivo, vasoplejía posoperatoria, necesidad de intubación orotraqueal y de tratamiento de reemplazo renal. La calidad se evalúo con la herramienta ROBINS.
ResultadosSe incluyeron tres estudios no aleatorizados, uno de un solo grupo. Hubo menos casos de mortalidad intrahospitalaria y a 30 días en el grupo en que no se suspendió el SV, sin una diferencia estadísticamente significativa. No hubo diferencia en la duración de la estancia hospitalaria o en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, intubación orotraqueal, necesidad de reemplazo renal, ni en la frecuencia de vasoplejía posoperatoria (OR = 0,77; IC 95%, 0,23-2,98).
ConclusionesLa evidencia actual es escasa y de baja calidad, por lo que no se puede generar una recomendación respecto al uso del SV previo a cirugía cardiaca, se requiere realización de estudios adicionales.
Sacubitril/valsartan (SV) is the first drug approved for clinical use that inhibits neprilysin and angiotensin receptor. It is recommended in patients with heart failure because it reduces the risk of hospitalization due to heart failure decompensation and mortality.1,2
There is growing concern about SV use in patients undergoing cardiac surgery since some cases of postoperative vasoplegia have been reported, suggesting that the drug could lead to worse clinical outcomes, such as increased mortality, increased hospital stay, and acute kidney injury.3–5 The recommendations on the use of SV until surgery are controversial, but since it shares some mechanisms of action with inhibitors of the renin angiotensin system (RAAS), some guidelines recommend its withdrawal.6
The objective of this systematic review of the literature is to assess whether, in the perioperative period of patients undergoing cardiac surgery, the use of SV compared with never having used it or its withdrawal is associated with worse clinical outcomes to support and facilitate clinical decision-making.
MethodsWe conducted a systematic literature review of randomized clinical trials and nonrandomized studies, following specific recommendations to include this kind of evidence.7 The study was approved by the ethics committee and the protocol was published in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) registry CRD42023394036.
To be included studies had to evaluate patients older than 18 years, undergoing cardiac surgery (heart transplant, coronary artery bypass graft, heart valve replacement, or any other cardiac surgery), and compare the use of SV up to the day of surgery versus stopping or not starting it prior to the procedure. Additionally, single-arm descriptive studies reporting on the use of SV in the perioperative period were included.
Studies in which it was not possible to individualize which treatment arm each patient belonged to, were excluded. Those who evaluated procedures such as transcatheter aortic valve implantation, percutaneous mitral valve repair, pericardiotomy, pericardiocentesis, or pericardial window were also excluded.
Studies had to report at least 1 of the following outcomes: in-hospital mortality, 30-day all-cause mortality, length of stay in the intensive care unit or general ward, duration of orotracheal intubation, requirement for renal replacement therapy, and postoperative vasoplegia (defined as the need for vasopressor within 48h after the surgical procedure to maintain a mean arterial pressure above 65mmHg in the absence of cardiogenic or hemorrhagic shock or sepsis). The definition of postoperative vasoplegia varies in literature; however, the most frequently described criteria are used.5
The search was performed on November 21, 2022, in PubMed (MedLine), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), EMBASE (Elsevier), and LILACs. Studies published in Spanish and English were included with no time limit. The search terms included: (“Neprilysin” OR “sacubitril and valsartan sodium hydrate drug combination” OR “neprilysin antagonists and inhibitors”) AND (“Cardiac Surgical Procedures” OR “Thoracic Surgery” OR “Coronary Artery Bypass” OR “Cardiovascular Surgical Procedures” OR “Heart Transplantation” OR “Myocardial Revascularization” OR “Heart Valve Prosthesis Implantation”). The complete search strategy is presented in the supplementary data. Additionally, we searched for cross-references between the identified articles and reviews. Duplicate references have been removed.
Two researchers (L. Gilón and V. Dávila) independently reviewed the titles and abstracts of each retrieved record and evaluated the full texts of all potentially eligible articles. All discrepancies were identified and resolved by consensus or by a third investigator (Ó. Muñoz). After the initial selection, 2 reviewers independently performed a quality assessment of the non-randomized trials using the ROBINS I (L. Gilón, V. Dávila) tool.8 This tool allows the classification of the risk of global bias for each study and each outcome, defining it as “low,” “moderate,” “serious” or “critical,” according to 3 study temporality domains “before the intervention,” “at the time of the intervention” and “after the intervention,” with special emphasis on identifying possible selection biases.8 For randomized studies, we planned to use the Cochrane collaboration tool in version 2 (RoB2), in which the risk of bias was classified as low/high.9
The extraction of the relevant data from each study was paired. The following data were extracted: year of publication, type of study, author, number of participants, age, sex, body mass index, intervention and comparison, concomitant use of other medications, type of cardiac surgery, preprocedural ejection fraction, length of hospital stay, and previously defined outcome data.
A meta-analysis of the information was planned if the clinical heterogeneity was low using the Review Manager (RevMan) software (Cochrane, United Kingdom), recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration. Otherwise, we plan to synthesize the information through comparative tables for each evaluated outcome.
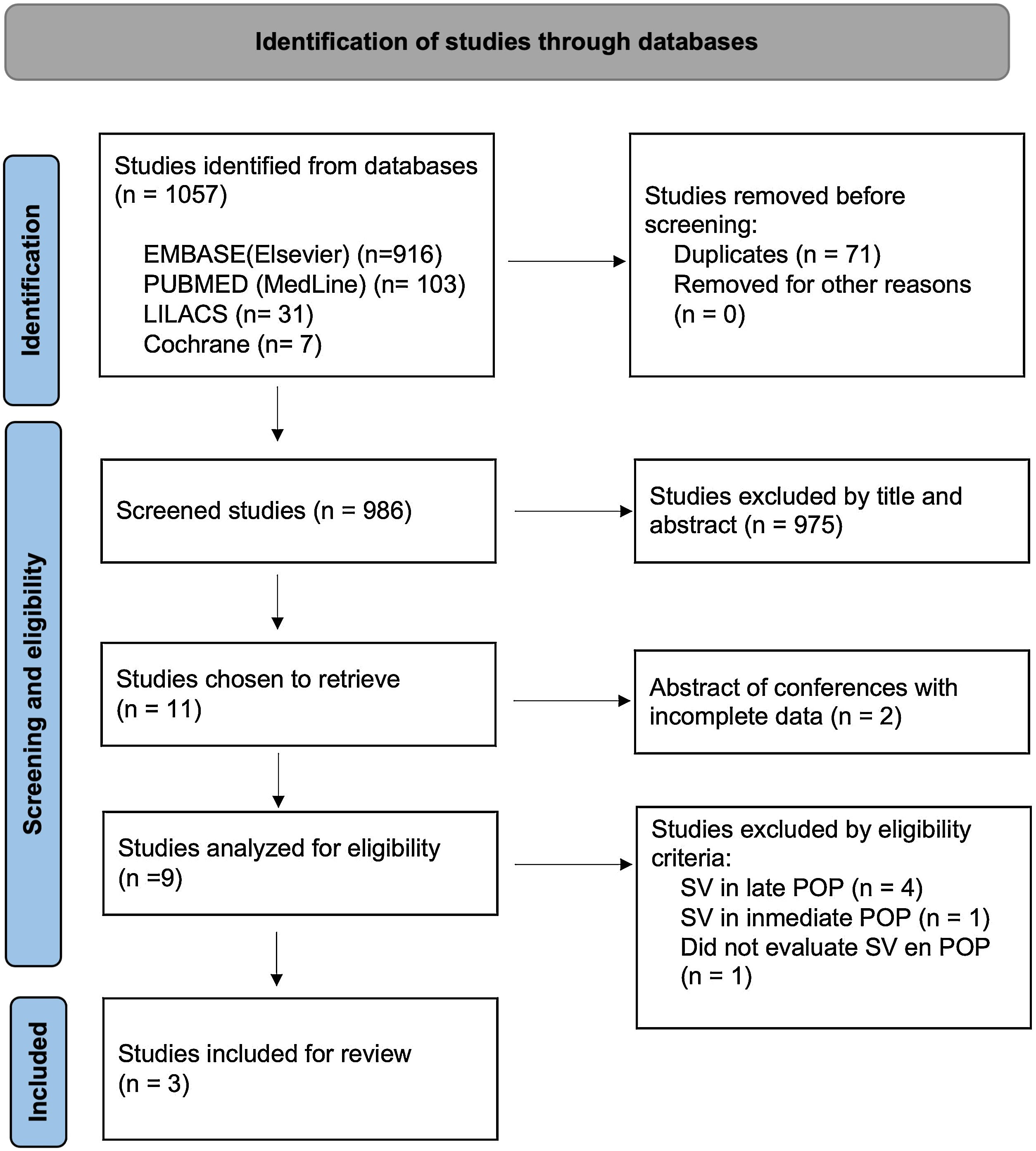
ResultsDescriptive resultsA total of 1057 articles were identified, of which 3 were included in the final analysis. The selection process is presented in the PRISMA diagram (Fig. 1). The studies analyzed for eligibility, but not included, are presented in Table 1 of the supplementary data. The 3 included studies were non-randomized; of these, 1 was a single-arm analysis. The characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies
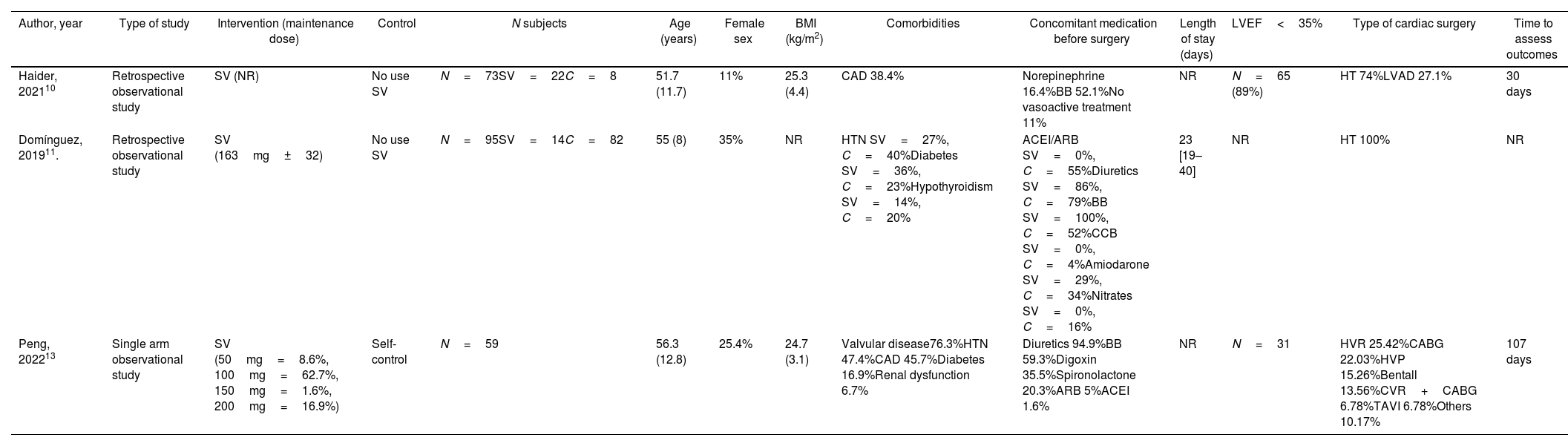
| Author, year | Type of study | Intervention (maintenance dose) | Control | N subjects | Age (years) | Female sex | BMI (kg/m2) | Comorbidities | Concomitant medication before surgery | Length of stay (days) | LVEF<35% | Type of cardiac surgery | Time to assess outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haider, 202110 | Retrospective observational study | SV (NR) | No use SV | N=73SV=22C=8 | 51.7 (11.7) | 11% | 25.3 (4.4) | CAD 38.4% | Norepinephrine 16.4%BB 52.1%No vasoactive treatment 11% | NR | N=65 (89%) | HT 74%LVAD 27.1% | 30 days |
| Domínguez, 201911. | Retrospective observational study | SV (163mg±32) | No use SV | N=95SV=14C=82 | 55 (8) | 35% | NR | HTN SV=27%, C=40%Diabetes SV=36%, C=23%Hypothyroidism SV=14%, C=20% | ACEI/ARB SV=0%, C=55%Diuretics SV=86%, C=79%BB SV=100%, C=52%CCB SV=0%, C=4%Amiodarone SV=29%, C=34%Nitrates SV=0%, C=16% | 23 [19–40] | NR | HT 100% | NR |
| Peng, 202213 | Single arm observational study | SV (50mg=8.6%, 100mg=62.7%, 150mg=1.6%, 200mg=16.9%) | Self-control | N=59 | 56.3 (12.8) | 25.4% | 24.7 (3.1) | Valvular disease76.3%HTN 47.4%CAD 45.7%Diabetes 16.9%Renal dysfunction 6.7% | Diuretics 94.9%BB 59.3%Digoxin 35.5%Spironolactone 20.3%ARB 5%ACEI 1.6% | NR | N=31 | HVR 25.42%CABG 22.03%HVP 15.26%Bentall 13.56%CVR+CABG 6.78%TAVI 6.78%Others 10.17% | 107 days |
ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BB, beta-blocker; BMI, body mass index; C, control; CAD, coronary artery disease; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; CCB, calcium channel block; CKD, chronic kidney disease; HT, heart transplantation; HTN, hypertension; HVP, heart valvuloplasty; HVR, heart valve replacement; LVEF, left ventricle ejection fraction; LVAD, left ventricular assist device; NR, not reported; SV, sacubitril/valsartan; TAVI, transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
Data are expressed as no. (%) or median [interquartile range].
The average age was similar in the 3 studies (51.7–56.3 years), and the majority were men. The most frequent procedure was heart transplantation, and the most frequently used concomitant medications were diuretics and beta blockers.
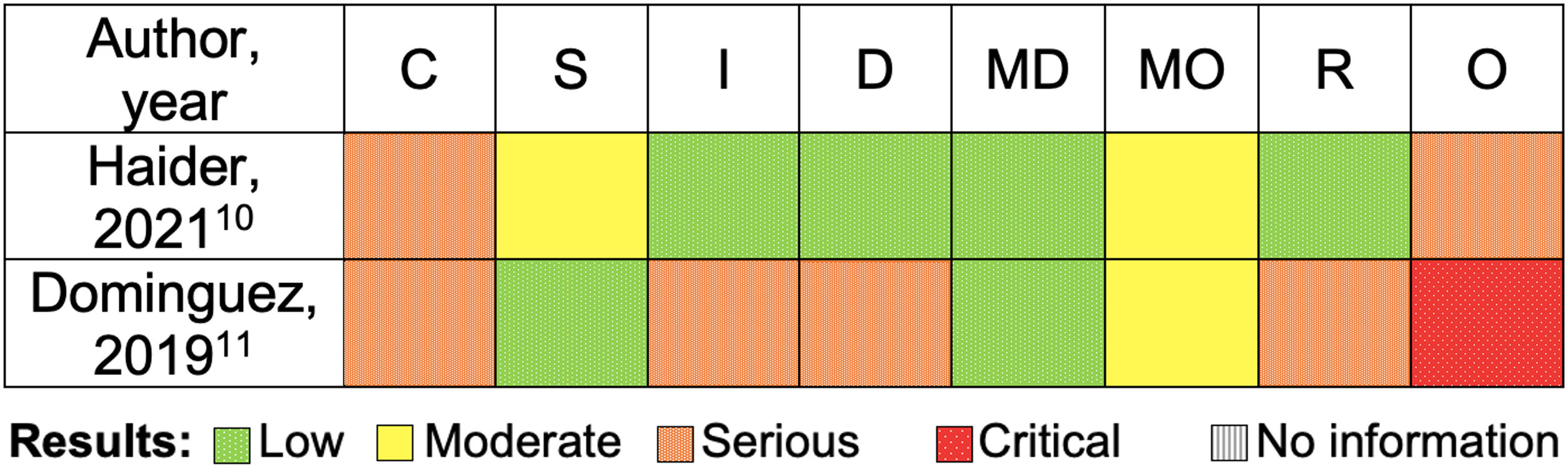
Quality assessmentRegarding confounding factors, factors such as age, weight and use of concomitant medications were not considered in any of the studies. In 1 study10 no information was found on the timing of initiation and discontinuation of SV, and there was a systematic error since the blood volume status of the patients was not known, which could affect the definition of vasoplegia. In another study11 there was a significant difference between the 2 groups (patients in the SV group had INTERMACS III/IV more frequently compared to the control group), additionally in the intervention group the SV was suspended for approximately 20h before the procedure, which could have influenced the outcomes. In both studies,10,11 the investigators knew the patients who had received each intervention. An overview of the risk of bias in individual studies is presented in Fig. 2.
Risk of bias assessment (ROBINS-I): non-randomized trials. C, bias due to confounding; D, bias due to deviations from intended interventions; I, bias in classification of interventions; MD, bias due to missing data; MO, bias due to measurement of outcomes; O, overall risk of bias; R, bias in selection of the reported result; S, bias in selection of participants into the study.
The quality assessment of the evidence was carried out using the GRADE tool,12 the synthesis of the findings is presented in Table 2 of the supplementary data, the quality of the evidence was classified as very low.
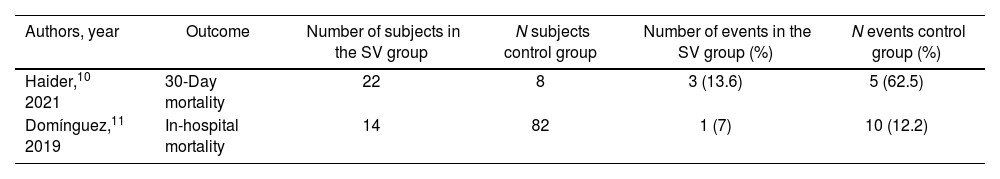
Clinical outcomesIn-hospital and 30-day mortalityOne study10 reported 30-day mortality and another study11 reported in-hospital mortality, with lower mortality ratios in the group with use of SV up to the day of surgery (Table 2). Given the small number of events, the differences between both groups were not statistically significant.
In-hospital and 30-day mortality
| Authors, year | Outcome | Number of subjects in the SV group | N subjects control group | Number of events in the SV group (%) | N events control group (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haider,10 2021 | 30-Day mortality | 22 | 8 | 3 (13.6) | 5 (62.5) |
| Domínguez,11 2019 | In-hospital mortality | 14 | 82 | 1 (7) | 10 (12.2) |
Control group, SV stopped or not started prior to the procedure. SV group, use of SV up to the day of surgery. SV, sacubitril/valsartan.
Data are expressed as no. (%).
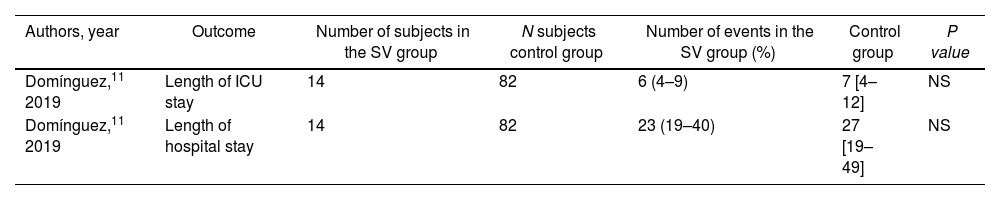
The length of stay in the intensive care unit and overall hospitalization was reported in only 1 study,11 without significant differences. The data is presented in Table 3.
Hospitalization and intensive care unit duration
| Authors, year | Outcome | Number of subjects in the SV group | N subjects control group | Number of events in the SV group (%) | Control group | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domínguez,11 2019 | Length of ICU stay | 14 | 82 | 6 (4–9) | 7 [4–12] | NS |
| Domínguez,11 2019 | Length of hospital stay | 14 | 82 | 23 (19–40) | 27 [19–49] | NS |
Control group, SV stopped or not started prior to the procedure. SV group, use of SV up to the day of surgery. ICU, intense care unit; SV, sacubitril/valsartan.
Data are expressed as no. (%) or median [interquartile range].
Domínguez et al.11 reported the duration of orotracheal intubation without finding differences between the 2 groups.
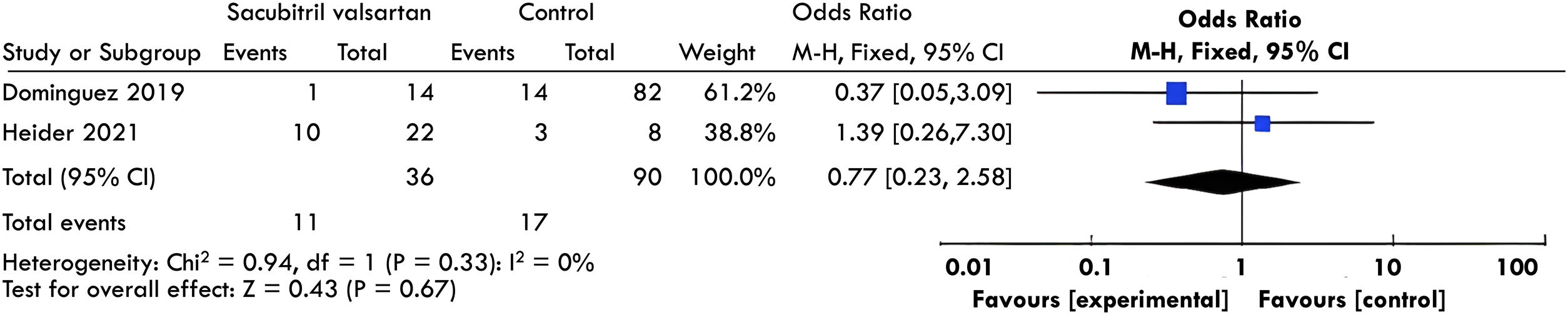
Postoperative vasoplegiaTwo studies10,11 evaluated postoperative vasoplegia. A meta-analysis of these results was performed without finding a significant difference between both groups (OR, 0.77; 95%CI, 0.23–2.98; I2; 0%, see Fig. 3).
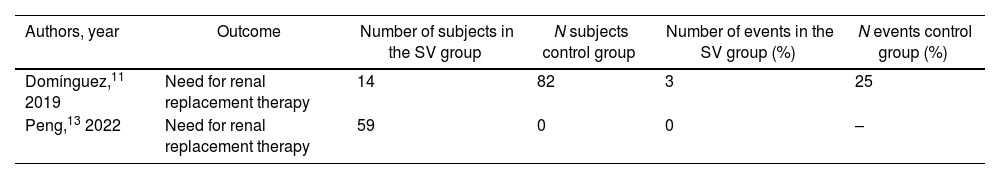
Renal replacement therapyThis outcome was reported in 2 studies.11,13 However, one of these13 was a single-arm study without a control group. Domínguez et al.11 reported the need for renal replacement in 21.4% of the patients in the group using SV up to the day of surgery versus 30.5% in the group with SV stopped or not started prior to the procedure. In the study by Peng et al.13 no patients required renal replacement therapy (Table 4).
Renal replacement therapy
| Authors, year | Outcome | Number of subjects in the SV group | N subjects control group | Number of events in the SV group (%) | N events control group (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domínguez,11 2019 | Need for renal replacement therapy | 14 | 82 | 3 | 25 |
| Peng,13 2022 | Need for renal replacement therapy | 59 | 0 | 0 | – |
Control group, SV stopped or not started prior to the procedure. SV group, use of SV up to the day of surgery. SV, sacubitril/valsartan.
Data are expressed as no. (%).
The use of foundational therapy in heart failure (SV, beta-blocker, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, and SGLT2i), particularly in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, has shown excellent benefits in reducing adverse clinical outcomes and improving function and quality of life, with favorable results in reverse cardiac remodeling, increased left ventricular ejection fraction, and metabolic recovery of the heart.14 However, patients with these therapies must undergo cardiac surgical procedures, and there is still controversy regarding the perioperative management of these drugs.
The use of SV until the day of cardiac surgery versus its discontinuation beforehand remains controversial. The present systematic review was carried out using information published to date. We found a few studies with a high risk of bias, mainly associated with selection bias. Although a trend in benefit in terms of mortality was observed, evidence is insufficient to recommend the use or withdrawal of SV in this setting.
Regarding mortality, 1 study10 reported that the 30-day mortality rate was lower in patients receiving SV (13.6% vs 62.5% in the control group); however, there was inadequate control of confounding factors, so the quality of evidence was very low.
Regarding the other outcomes, it was only possible to perform a meta-analysis of the information regarding the incidence of vasoplegia without finding a significant difference between the intervention and control groups. However, as previously mentioned, the quality of the information was low and imprecise given the minimal number of outcomes. Additionally, no difference was found in the number of days of stay in the general ward or intensive care unit. Regarding the need for renal replacement therapy, no difference was found between the intervention and control group, which was evaluated in 2 studies, one of these with a single arm study,13 in the other11 bias was found due to inadequate control of confounding factors and intervention bias, so the evidence is very low.
These findings show that there is no conclusive evidence to make a recommendation in favor of continuing medication or withdrawing it in the perioperative period. Therefore, a multidisciplinary team (heart team) of experts in the area should make decisions based on the particularities of each case.
LimitationsThe main limitation of our study is the scant evidence with a high risk of bias, which does not allow the generation of strong recommendations. In addition, most of the surgeries corresponded to cardiac transplantation, which makes it difficult to extrapolate the results to other more frequent cardiac surgeries, such as valve replacement or coronary artery bypass graft, which were minimally represented.10,11 Our study identified a gap in knowledge with a lack of high-quality evidence. Randomized clinical trials with larger sample sizes and a better representation of different types of procedures are needed to answer this question.
ConclusionsThis study shows that there is little low-quality evidence evaluating the use of SV in the perioperative period of patients undergoing cardiac surgery. A recommendation for the use or discontinuation of SV cannot be made in this setting. Future randomized clinical trials are needed to resolve this question; meanwhile, a multidisciplinary team should make the decision.
- -
Postoperative vasoplegia is associated with increased mortality.
- -
There is growing concern about SV use in patients undergoing cardiac surgery since some cases of postoperative vasoplegia have been reported.
- -
The recommendations on the use of SV until surgery are controversial, without clear evidence.
- -
This study highlights a knowledge gap regarding the perioperative use of SV.
- -
The use of SV in the perioperative period may be safe; however, future randomized clinical trials are needed.
None.
Ethical considerationsAll authors attest that they comply with the Human Studies Committee. All international recommendations regarding clinical investigations were followed, as well as the STROBE and PRISMA guidelines. No informed consent was necessary as this is a systematic review. Potential sex and gender biases were not considered, as this is a systematic review. However, sex was considered within the population characteristics.
Statement on the use of artificial intelligenceNo artificial intelligence was used.
Authors’ contributionsAll authors participated in the design of the protocol and analysis of data, the drafting the work and gave their final approval of the version to be published. L. Gilón was in charge of conception, design, data acquisition, drafting the work and final approval. V. Dávila was in charge of the design, data acquisition, drafting the work and final approval. Ó. Muñoz, Á. García and E. Cáceres were in charge of the design of the protocol and analysis of data, and final approval of the version to be published.
Conflicts of interestAll authors report that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper.