QTc interval alterations have been described in patients receiving sofosbuvir. Our objective was to evaluate the effect of anti-hepatitis C virus drugs on the human cardiac conduction system.
MethodsWe included all patients with hepatitis C virus infection that started treatment with direct-acting antivirals in a tertiary hospital between May 2016 and March 2017. Three electrocardiograms were performed in them: before starting treatment; during treatment; and at least 3 weeks after finished treatment. Heart rate, PR, QRS, and QTc intervals were compared between patients with and without sofosbuvir. Patients were followed for a mean time of 41.9 weeks.
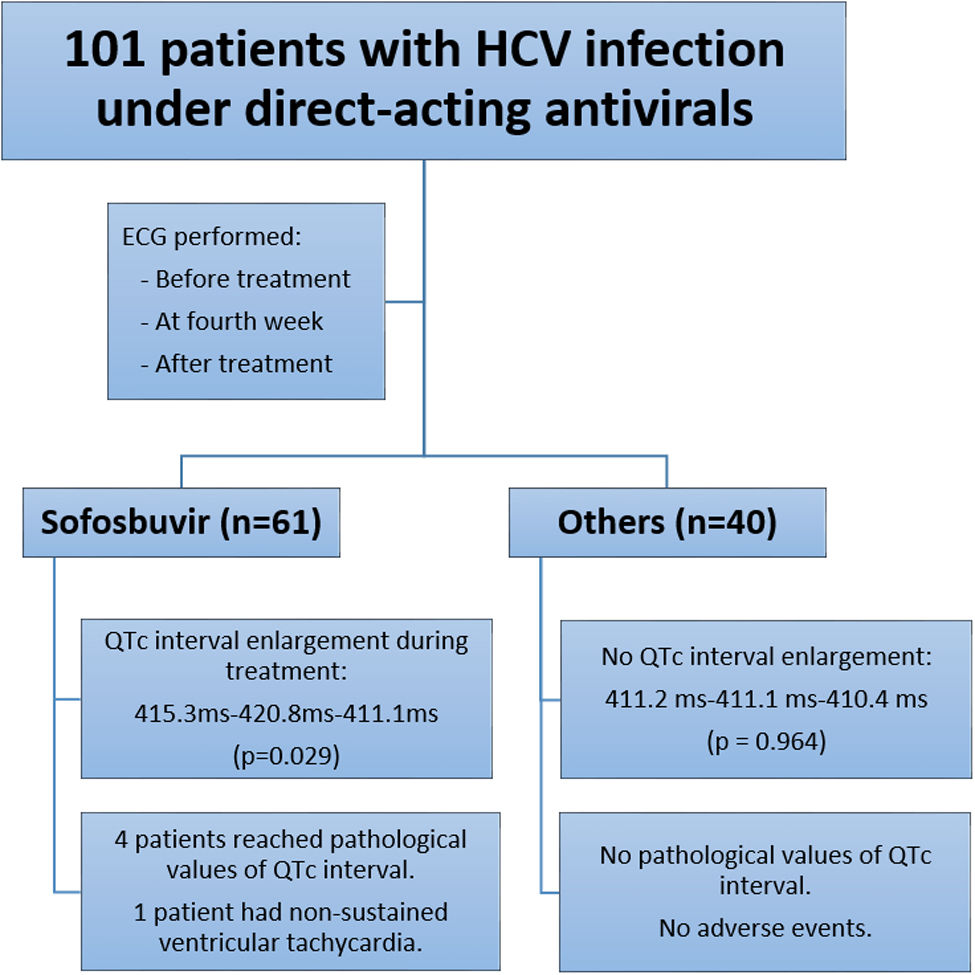
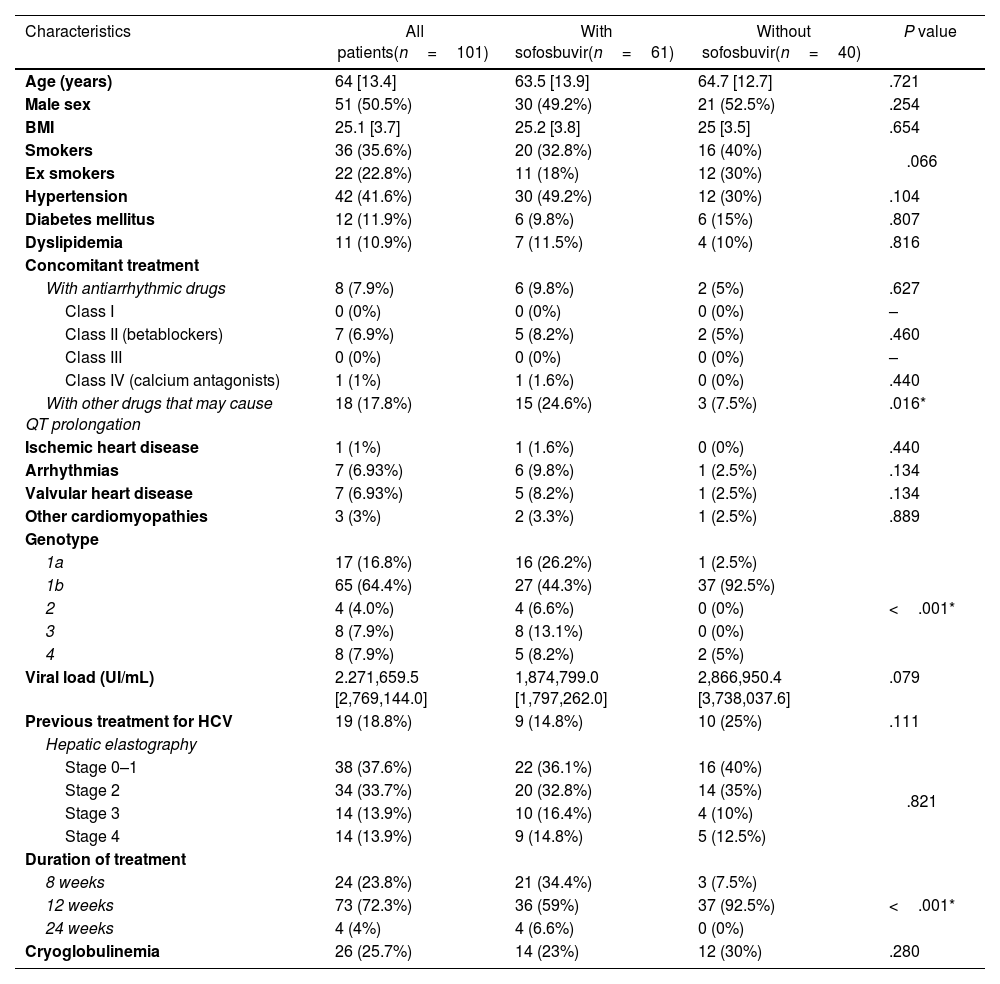
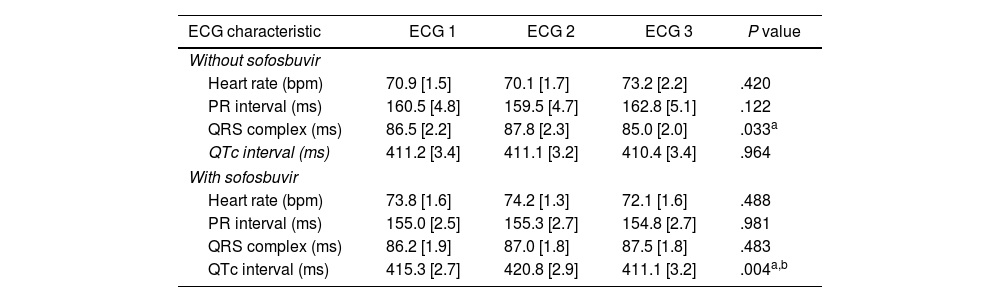
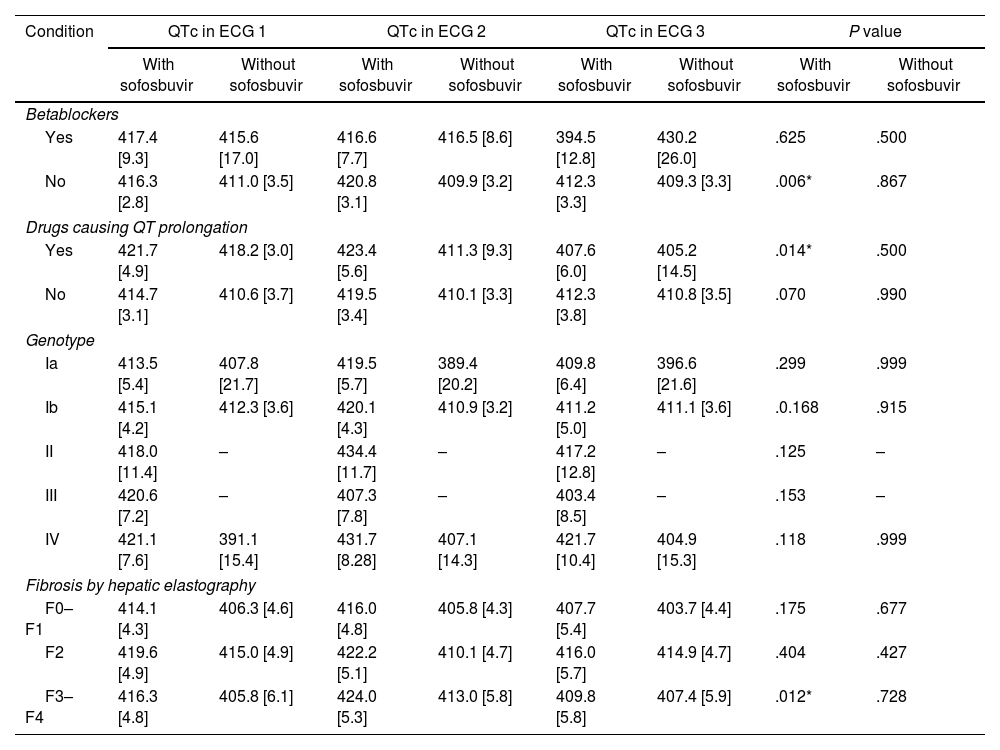
ResultsA total of 101 patients were studied, 61 received treatment with sofosbuvir and 40 without sofosbuvir. No differences were found between the 2 groups regarding heart rate, and PR intervals. There was a statistically significant enlargement of QTc in patients with sofosbuvir at the fourth week of treatment (415.3ms vs 420.8ms) that returned to baseline values once finalized (411.1ms; P=.029). These differences were not observed in patients without sofosbuvir.
ConclusionsWe observed a statistically significant prolongation of the QTc interval at the fourth week of treatment in patients with sofosbuvir, which returned to baseline levels once the treatment was finished. Further prospective studies are needed to assess the clinical relevance of these findings.
Se han descrito alteraciones del intervalo QTc en pacientes en tratamiento con sofosbuvir. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar el efecto de los fármacos contra el virus de la hepatitis C sobre el sistema de conducción cardiaca humana.
MétodosIncluimos a todos los pacientes con infección por VHC que iniciaron tratamiento con antivirales de acción directa en un hospital terciario entre mayo de 2016 y marzo de 2017. Se les realizaron 3 electrocardiogramas: antes de iniciar el tratamiento, durante el tratamiento y al menos 3semanas después de finalizar el tratamiento. Se compararon la frecuencia cardiaca y los intervalos PR, QRS y QTc entre pacientes con y sin sofosbuvir. Se siguió a los pacientes durante un tiempo medio de 41,9semanas.
ResultadosSe estudió a 101 pacientes, de los que 61 recibieron tratamiento con sofosbuvir y 40 sin sofosbuvir. No se encontraron diferencias entre los 2 grupos en cuanto a la frecuencia cardiaca y los intervalos PR. Se observó un aumento estadísticamente significativo del intervalo QTc en los pacientes con sofosbuvir en la cuarta semana de tratamiento (415,3ms frente a 420,8ms), que volvió a los valores basales una vez finalizado el tratamiento (411,1ms; p=0,029). Estas diferencias no se observaron en los pacientes sin sofosbuvir.
ConclusionesObservamos una prolongación estadísticamente significativa del intervalo QTc en la cuarta semana de tratamiento en los pacientes con sofosbuvir, que volvió a los niveles basales una vez finalizado el tratamiento. Se necesitan más estudios prospectivos para evaluar la relevancia clínica de estos hallazgos.
Article
Use datos de acceso a SEC en el menú Acceder.
Si es socio de la Sociedad Española de Cardiología y no puede acceder con sus claves, escriba a rec@cardioclinics.org.
Use the Society's website login and password here.
If you are member of SEC and you have some problems with your login data, please contact with rec@cardioclinics.org.