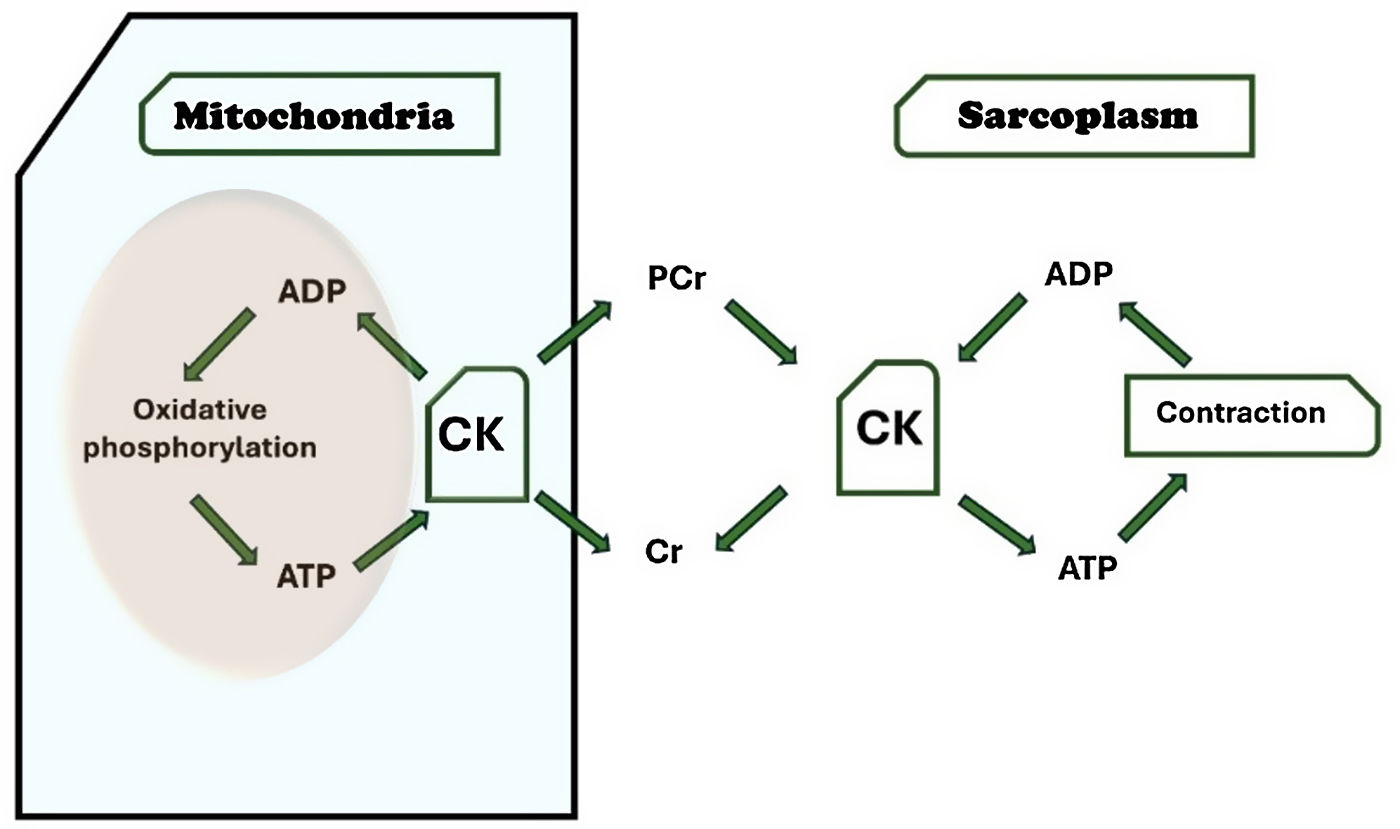
Heart failure (HF) poses a significant global health burden. Patients with HF experience reduced exercise tolerance, greatly affecting their quality of life. While creatine monohydrate (CM) improves functional capacity in healthy individuals, its effects in HF patients remain unexplored.
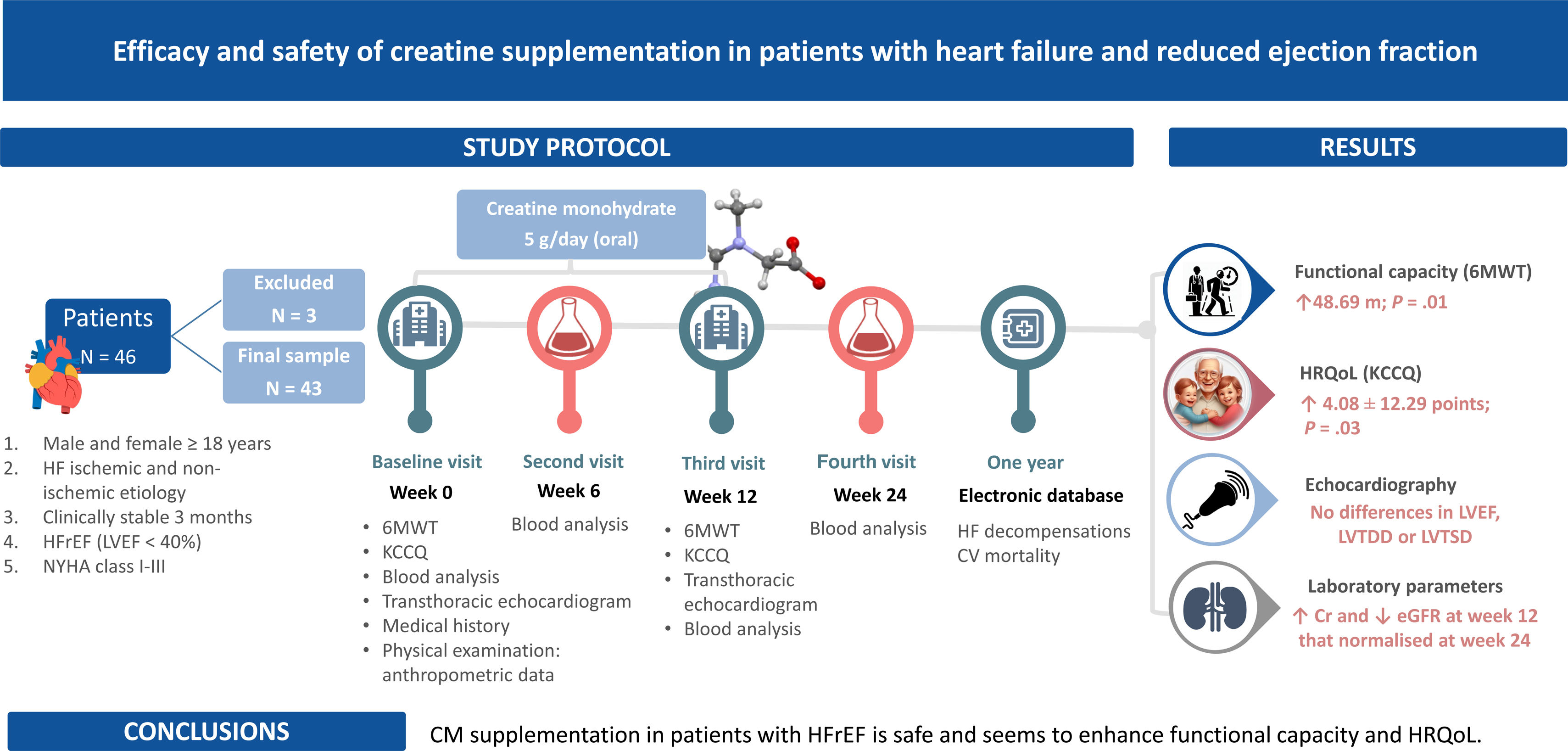
MethodsWe conducted an exploratory, prospective, single center, open-label study evaluating the efficacy and safety of 5g/day CM during 3 months in patients with HF and reduced ejection fraction. Outcomes included functional capacity, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), echocardiographic and laboratory parameters at 3-months and HF decompensations and mortality at 1-year.
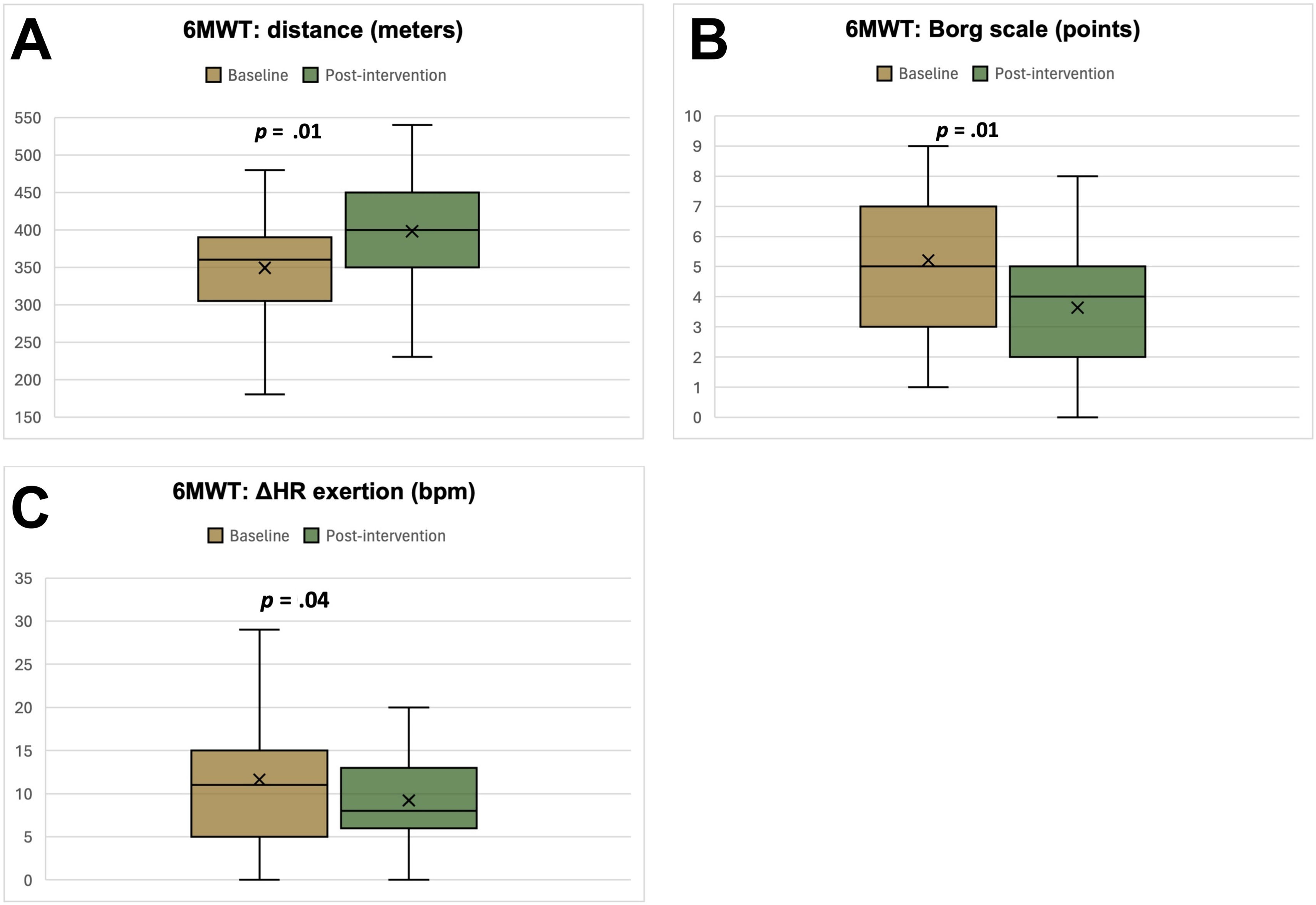
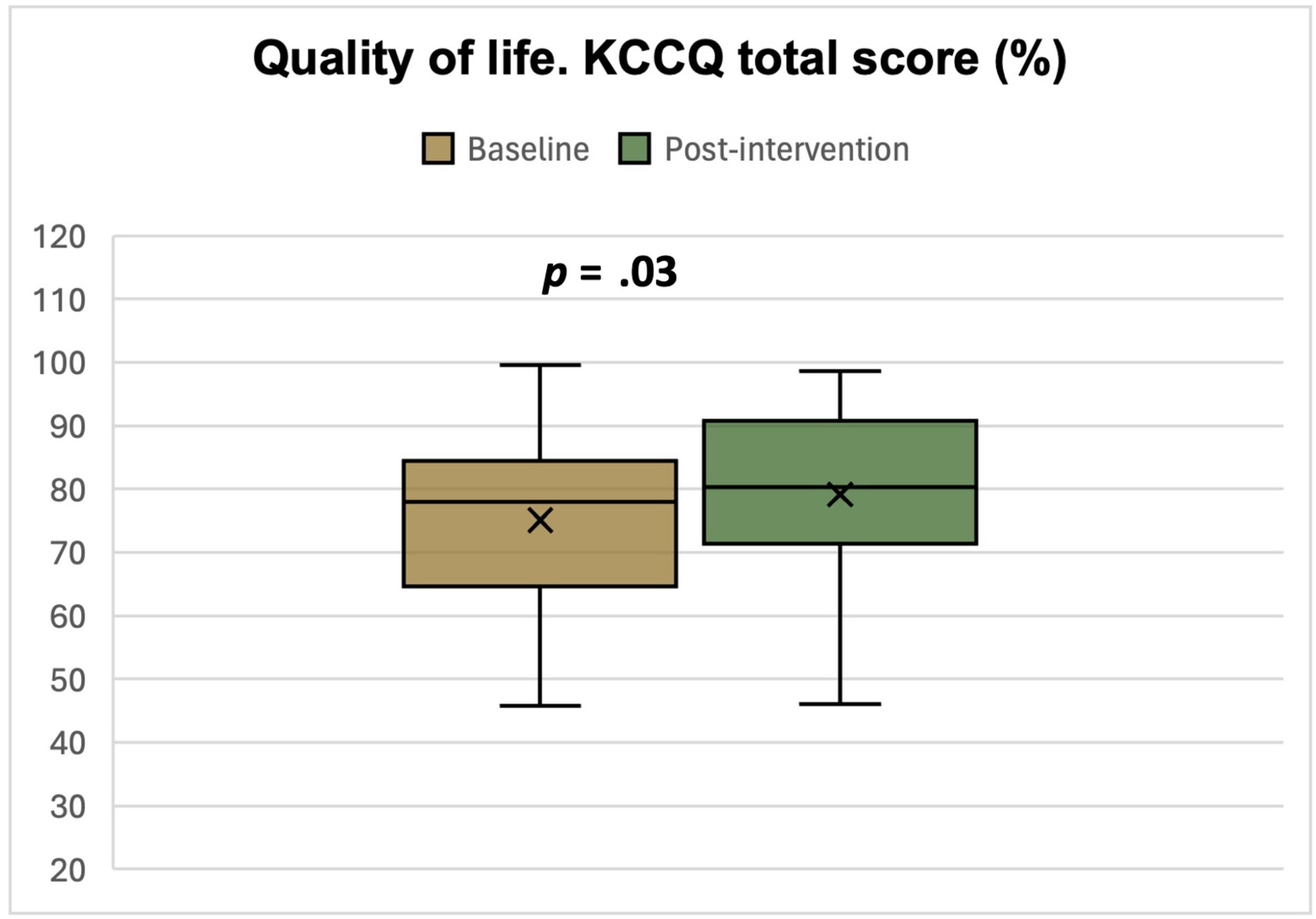
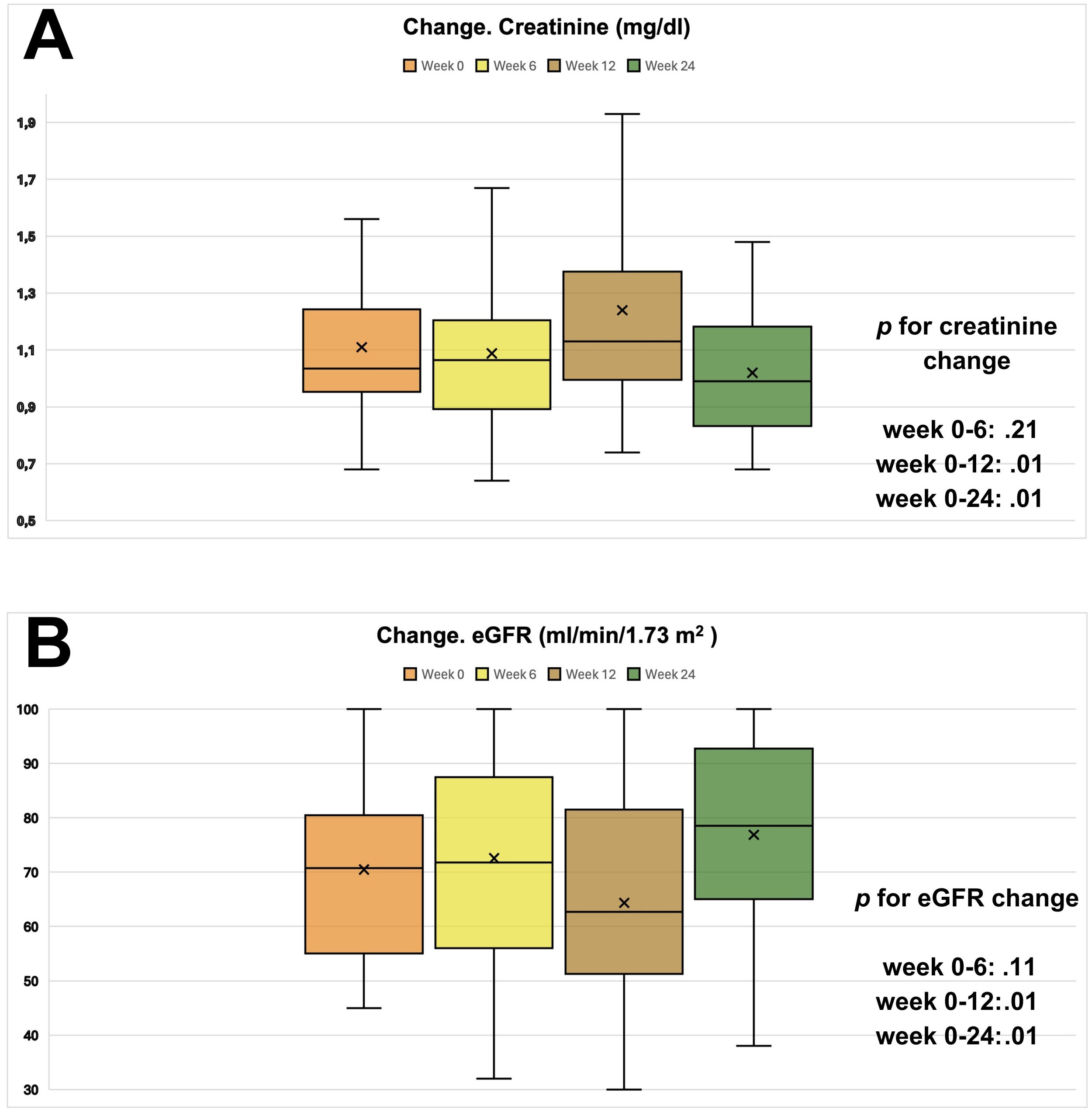
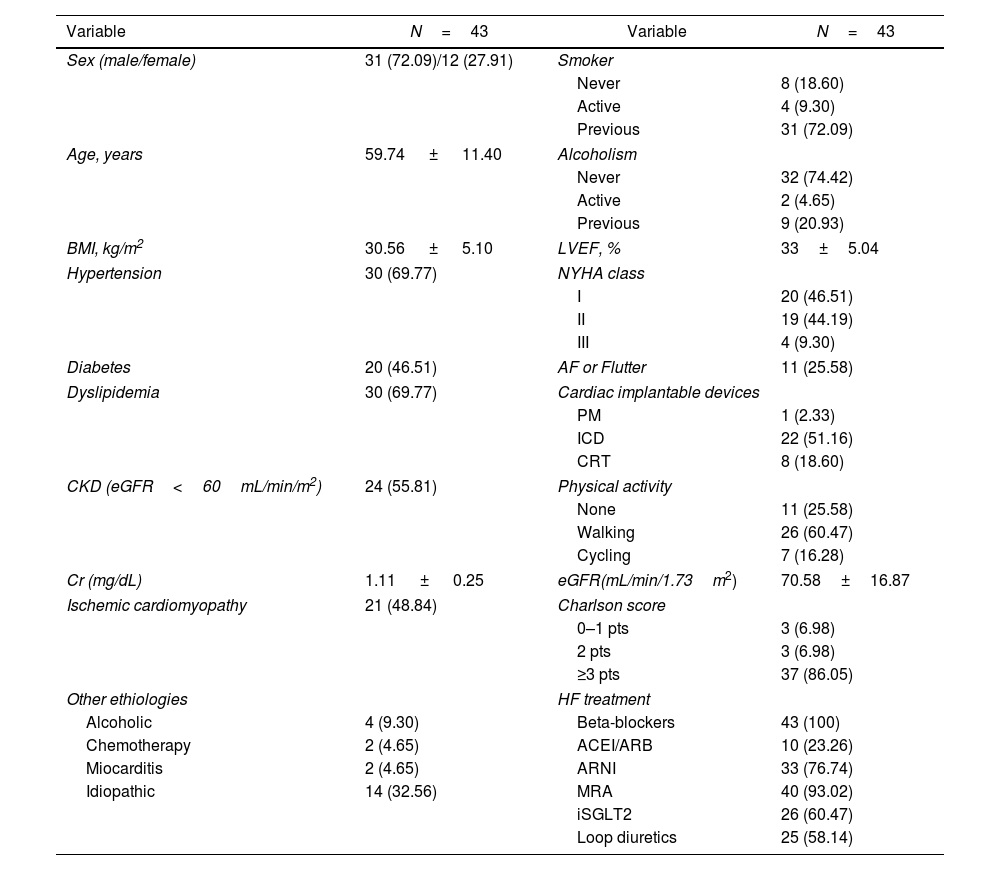
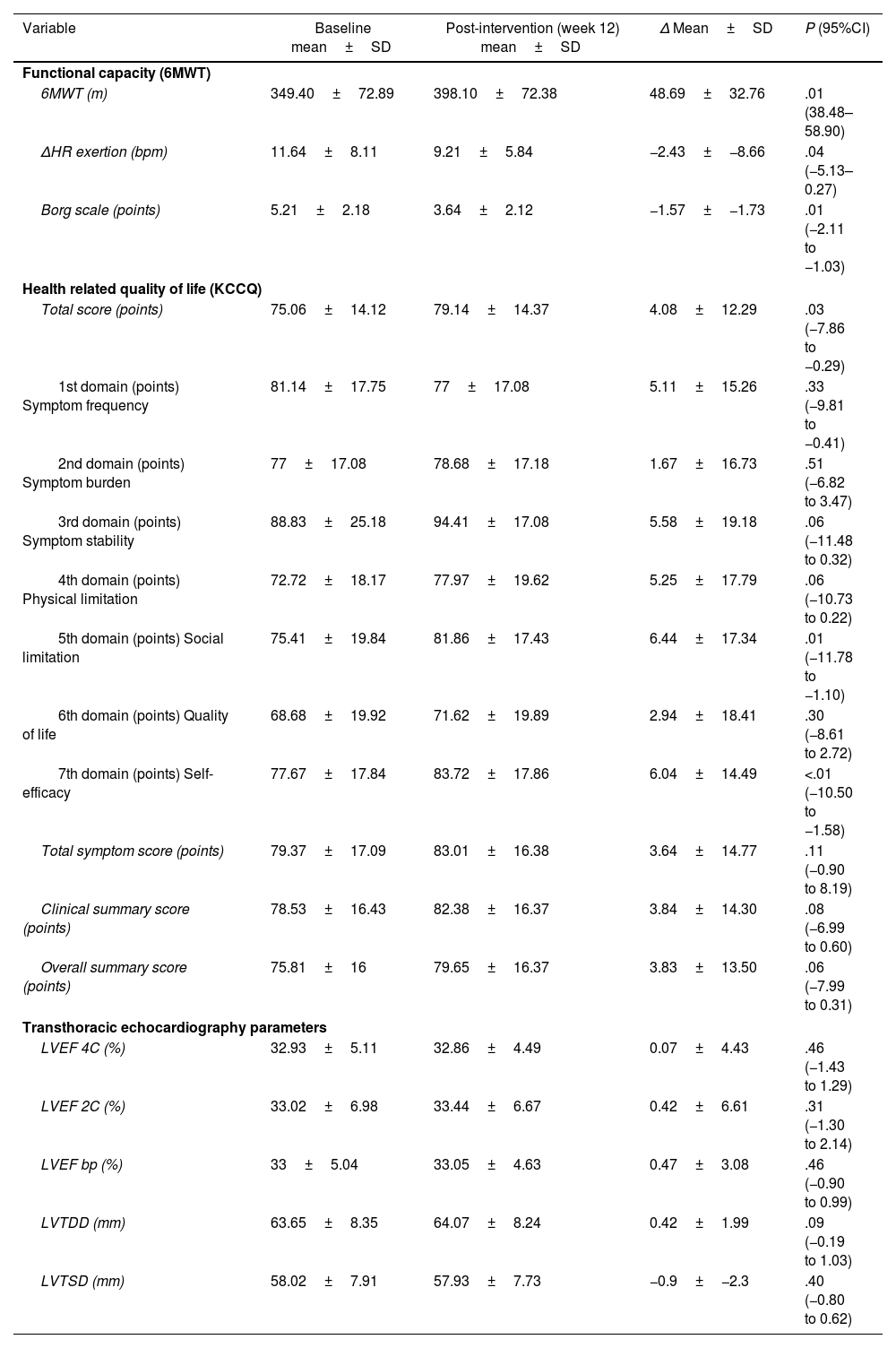
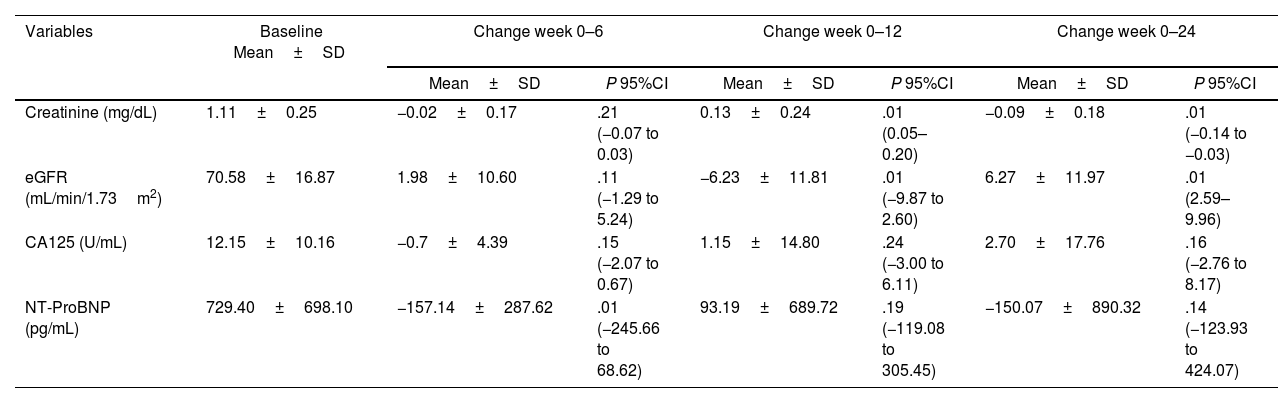
ResultsA total of 43 patients participated (60.73±11.73years; 30.43% females). The intervention was safe. Creatinine increased and glomerular filtration rate declined at 3 months but normalized after discontinuing CM. We observed a statistically significant increase in the 6-minute walk test (48.69±32.76; P=.005), a reduction in Borg scale exertion (−1.57±−1.73 points; P<.01), and decreased heart rate increment during exercise (−2.43±−8.66bpm; P=.04). HRQoL improved significantly (4.08±12.29 points; P=.03). No changes were found in echocardiographic parameters, HF decompensations, or mortality.
ConclusionsCM supplementation in patients with HF and reduced ejection fraction is safe and could improve functional capacity and HRQoL. Further research is warranted to confirm our results.
La insuficiencia cardiaca (IC) constituye una pandemia que impacta en la salud pública global. Los pacientes con IC experimentan una reducción en la tolerancia al ejercicio que afecta su calidad de vida. El monohidrato de creatina (MC) mejora la capacidad funcional en individuos sanos, pero sus efectos en pacientes con IC no han sido explorados. El objetivo del estudio es evaluar la eficacia y seguridad del MC en la IC con fracción de eyección reducida.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio exploratorio, prospectivo, unicéntrico y abierto, con MC 5g/día durante 3 meses. Las variables de resultado fueron capacidad funcional, calidad de vida relacionada con la salud (CVRS) parámetros ecocardiográficos y de laboratorio a los 3 meses, así como reagudizaciones de IC y mortalidad al año.
ResultadosParticiparon 43 pacientes (60,73±11,73 años; 30,43% mujeres). La intervención fue segura. La creatinina aumentó y el filtrado glomerular disminuyó a los 3 meses, normalizándose al suspender el MC. Observamos un aumento estadísticamente significativo en el test de la marcha de seis minutos (48,69±32,76; p=0,005), una reducción en la escala de Borg (−1,57±−1,73 puntos; p<0,01) y una disminución del incremento de frecuencia cardiaca durante el ejercicio (−2,43±−8,66lpm; p=0,04). La CVRS mejoró significativamente (4,08±12,29 puntos; p=0,03). No se encontraron diferencias en parámetros ecocardiográficos, reagudizaciones o mortalidad.
ConclusionesEl MC en pacientes con IC y fracción de eyección reducida es seguro y podría mejorar la capacidad funcional y CVRS. Se necesitan más estudios para confirmar nuestros resultados.
Article
Use datos de acceso a SEC en el menú Acceder.
Si es socio de la Sociedad Española de Cardiología y no puede acceder con sus claves, escriba a rec@cardioclinics.org.
Use the Society's website login and password here.
If you are member of SEC and you have some problems with your login data, please contact with rec@cardioclinics.org.